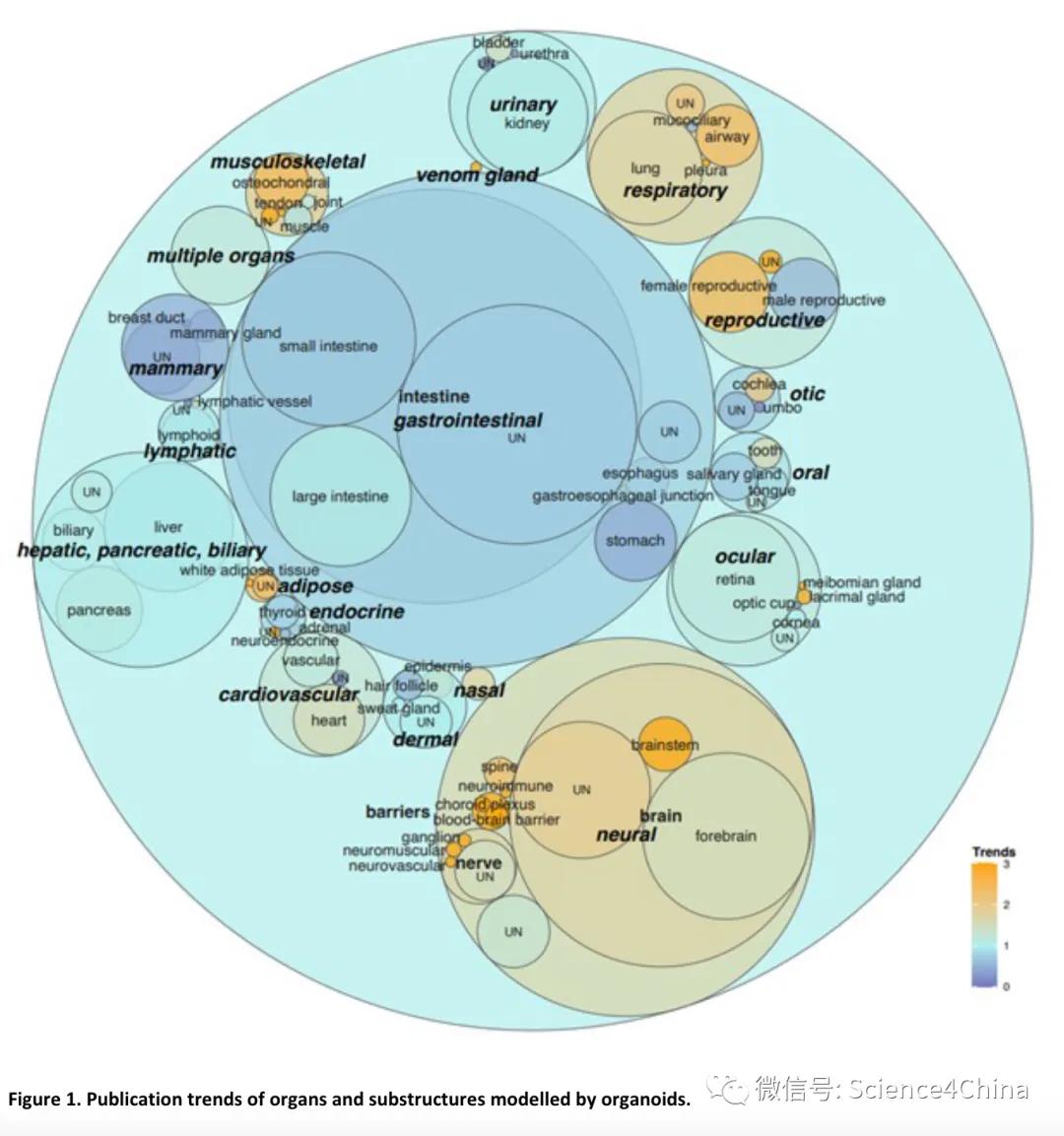
Since their birth in 2009, organoids have produced more than 16,000 documents, growing at an average annual growth rate of 50%. The heat of organoids is no less than that of Rosa Sea City, and its significance is also recognized.
In particular, the FDA and CFDA included organoid technology in the corresponding guideline document, and after the organoids were officially endorsed, the future is bright.
So what are the organoids?
Organoids are 3D or 2.5D structures cultured in vitro that have a similar structure and function to the organ of origin. Organoids are usually differentiated from adult stem cells or pluripotent stem cells, and they can be induced to differentiate into different organ types by different culture conditions.
Organoids are still in development, but they have shown great potential. With the continuous development of technology, organoids will play an increasingly important role in future medical research.
Organoids need to meet the following conditions:
Organoids are differentiated from stem cells or pluripotent stem cells
Organoids have a similar structure and function to their organs of origin
Organoids have many advantages, including:
Organoids can mimic organ development and function, which is important for studying disease mechanisms and drug development.
Organoids can differentiate from the patient's own stem cells or pluripotent stem cells, allowing them to be used in personalized medicine.
Organoids can be cultured rapidly and efficiently, allowing them to be used for large-scale drug screening.
Organoids can be used to study human organs in vitro, which can reduce animal experimentation.
Organoids have the following advantages over the 2D cell culture and small animal models:
Organoids have structures and functions closer to the organs in vivo.
Organoids can differentiate from the patient's own stem cells or pluripotent stem cells, allowing them to be used in personalized medicine.
Organoids can be cultured rapidly and efficiently, allowing them to be used for large-scale drug screening.
The core advantage of organoids is that they can more faithfully represent the real physiological state of the human body at a relatively low cost.
In other words, the data obtained in the organoid technology platform, with its specificity and sensitivity and direct human experiments, are very close.
People often say that time changes everything, and of course time also changes the organoids.
So the core question is, how long can this faithful representation of organoids last? The answer may not be as optimistic as expected.

This article (Jo et al., 2023) was originally a paper on the relationship between aging and intestine, but the author only used P0 generation of intestinal organoids for research, so it aroused the curiosity and attention of the master.
The authors used 80-week old mice and 6-10-week young mice to prepare intestinal organoids and compare the differences, but strangely only P0 generations.
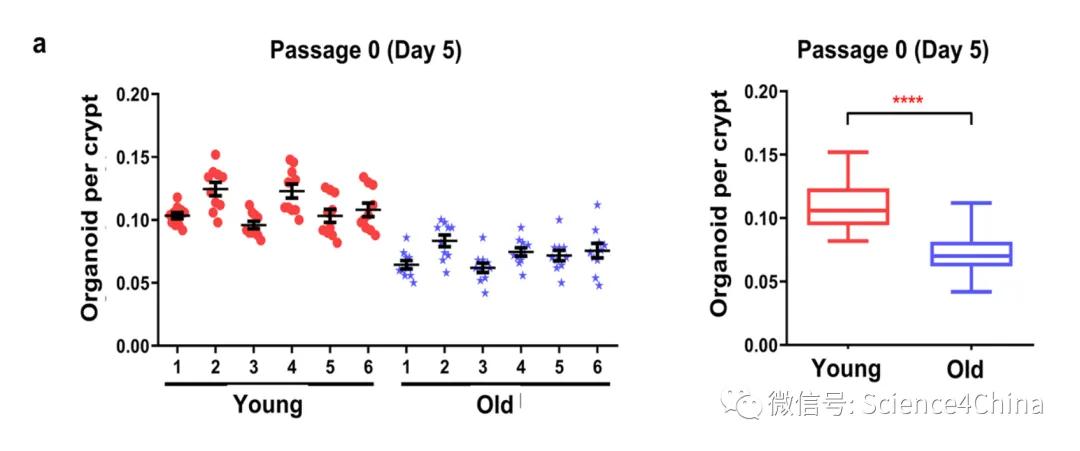
In terms of construction success rate, young mice were significantly higher than old mice.

There were also significant differences in the volume size of the organoids, which, by day 5, had become extremely apparent.
But the question is why only use the P0? The reason is that after a long period of culture, P2 (including P2), this difference is erased and disappeared, as shown in the figure below.
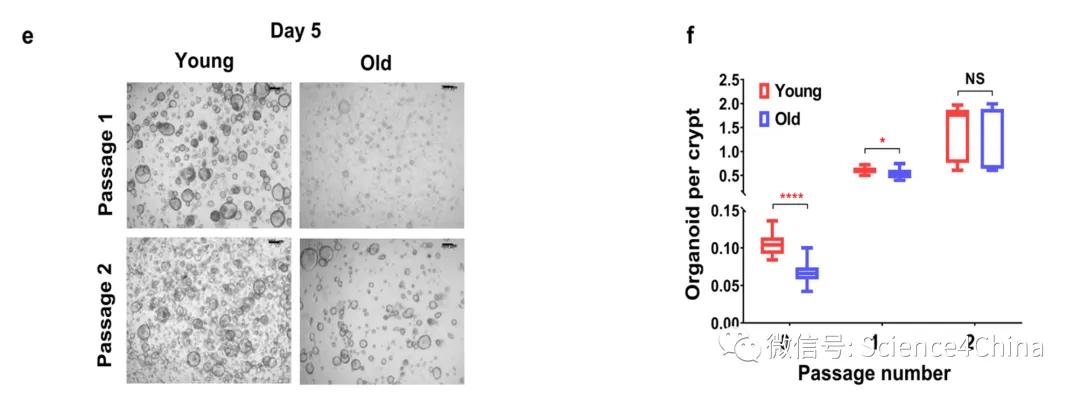
Can organoids only be faithful to P0~P1 for two generations? Why is this difference erased in culture? The medium itself supports the appreciation and expansion of intestinal stem cells, no surprise to rejuvenate aging intestinal stem cells in the process. After all, the reprogramming of the IPS can also reverse the state of the cells.
From another point of view, aging is a combination of many factors, without the aging niche, intestinal stem cells can restore youth. But in turn, if reversing one factor, can it reverse the whole aging? The heavenly master found it very difficult.
After all, although the difference of gene expression between old and young mouse organoids was found in the article, the key signaling pathway of TGF-beta was found, and the TGF-beta signal could be inhibited in organoids to achieve the effect of reversing aging, it was not realized in mouse, and it has no effect, so it is not necessary to publish the data.
Of course, there is no need for readers to panic. Organoids still have incomparable advantages, but when it comes to specific scientific problems, it still needs to carefully distinguish various influencing factors.
reference documentation
Jo, M.K., Moon, C.M., Jeon, H.-J., Han, Y., Lee, E.S., Kwon, J.-H., Yang, K.-M., Ahn, Y.-H., Kim, S.-E., Jung, S.-A., Kim, T.I., 2023. Effect of aging on the formation and growth of colonic epithelial organoids by changes in cell cycle arrest through TGF-β-Smad3 signaling.Inflamm Regener 43, 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41232-023-00282-6




