"Improved new drugs" in 2016 for the first time in the regulations, immediately became the industry research and development hotspot, all the way "wild" up to now, the clinical strategy has from blindly want BE / BA exemption confirmed clinical, the pursuit of improved "short frequency fast" yesterday, rapid development to strive to prove product safety / effectiveness advantage, the pursuit of "both clinical advantages and technical barriers" today. In order to avoid the "double blow" of original research and imitation products in the end market, on the one hand, it should save research and development costs through reasonable bridging research and accelerate the marketing; on the other hand, it is necessary to fully prove that the product has clear clinical advantages.2.3 type of new compound preparation project usually based on pathogenic factors, different mechanism of action, and the universality of the real world, etc., compared with other improved form, it is undoubtedly easier in clinical trials is better than the curative effect of modified alone, prove their clinical advantages, therefore, its research and development is getting more and more attention.
This paper integrates the relevant domestic and foreign regulations, guiding principles and literature clinical research requirements / suggestions for the development of new compounds, analyzes the relevant cases at home and abroad, and summarizes and refines the clinical research strategies of class 2.3 improved new drugs.
一、 Clinical strategy decision tree for the development of new compound preparations
China is transforming from a major pharmaceutical country to a major pharmaceutical country. In recent years, a large number of policies and regulations have been promulgated to encourage innovation. Innovative drug enterprises are developing rapidly, and generic drug enterprises are also actively transforming. However, the development of innovative drugs has high investment, high risk and long cycle. Improved innovation has become an important strategy for new drug enterprises to extend their product life cycle, and also become an important opportunity for the transformation of generic drug enterprises.
After the definition of improved new drugs was clarified in the Reform Plan of Chemical Drug Registration Classification in 2016, its research and development application witnessed explosive growth, but at the same time, it also exposed the problems of a large number of products were not obvious clinical advantages and serious homogenization competition. In 2020, the Technical Guidelines for Clinical Trials of Improved New Drugs for Chemical Drugs has further clarified the requirements for clinical advantages. Marked by the promulgation of these two key regulations, their development is roughly divided into three stages, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Development of improved new drugs in China
As shown in the figure above, the requirements of improved new drugs have been gradually clarified. Successful improved innovative products are not only the inevitable transformation product of a certain preparation technology or platform, but also a product that comprehensively applies synthesis and pharmaceutical research methods to prove its own clinical advantages in clinical research / application. Among them, the 2.3 type of improved new drugs are more multi-target, multi-mechanism and existing clinical experience developed as compound preparations, so it is easier to prove its advantages in safety / effectiveness in clinical trials, and become one of the hot directions of improvement. The clinical decision tree for developing marketed drugs into new compounds is shown in Figure 2.
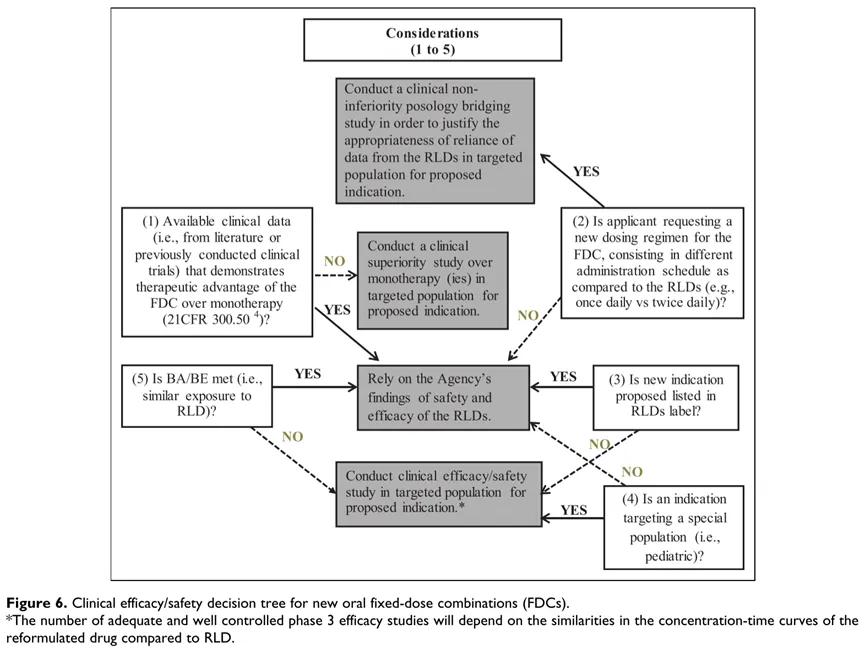
Figure 2: Decision tree for clinical development of new compound preparations
As shown in the figure above, in the development of a new compound preparation, with sufficient data / clinical experience, dosage, indications, patients are consistent with the modified drug, and BA / BE, the safety / effectiveness information of the marketed drug can be bridging. Otherwise, the corresponding dose study, safety, efficacy and other research contents should be completed [1].
The requirements for clinical research of compound preparations in domestic regulations and guidelines are similar to the above decision tree, but the new compound is further subdivided into: ① loading therapy: patients treated with any (or more) active components of the compound.② Initial treatment: patients who have not previously used any of the combination as monotherapy.③ Alternative therapy: The single dose level in the combination is the same as the dose of the single drug taken in a satisfactorily controlled patient.
Combining domestic and foreign regulations, guidelines and literature, the clinical research strategies for the development of new compound preparations are shown in Figure 3 [2][3]:
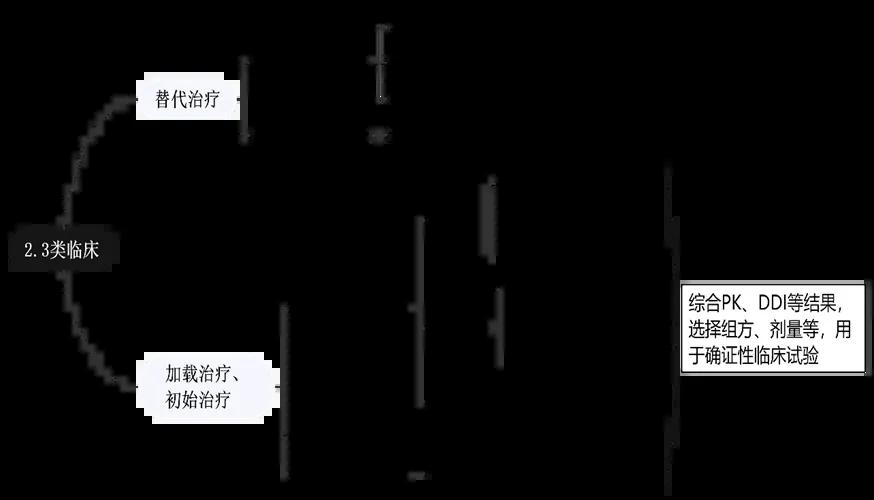
Figure 3: Clinical strategy for compound improvement as per relevant regulations / guidelines
As shown in the figure above, when complete safety / efficacy data are available and rich experience has been accumulated in clinical practice, and the dose / indication / patient are the same as those used alone, bridging existing data through BA / BE test can be considered, and confirmatory clinical trial [4] of compound preparation may no longer be needed. Generally, sufficient PK study, drug interaction (DDI study), dose-exposure-effect assessment and other studies should be carried out in the development of new compound, to formulate the dose, dose interval and prescription ratio, and complete the confirmatory clinical trial [3][5] with the preferred prescription, dose and regimen.
二、Related cases
1、Alternative treatment
FDA, the approved Kombiglyze XR is an approved product by path 505 (b) (2) and develops saxagliptin and metformin sustained release tablets as a combination. The clinical strategy of this product is bridging of safety / efficacy data for single agent and exemption from confirmatory clinical studies. The bridging path is shown in the following figure [6]:
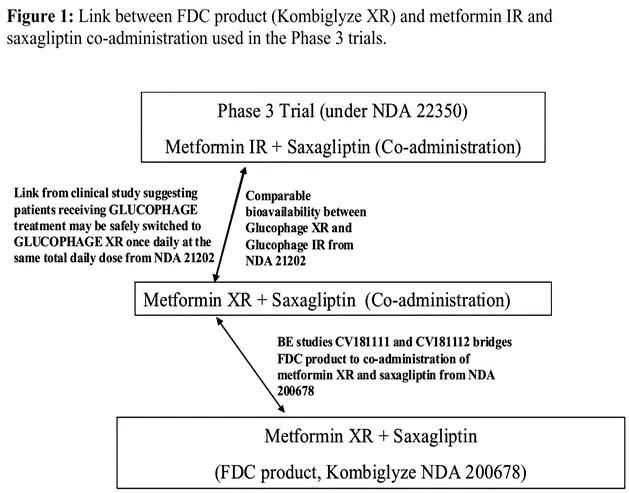
Figure 4: Clinical bridging strategy of saxagliptin metformin sustained-release tablets
As shown in the figure above, the product is not changed in the modified indication, dose, and patient population. The key data cited include: the development of metformin sustained-release tablets has demonstrated that the extended-release tablets and metformin (rapid release) preparations have consistent bioavailability in the body and equivalent efficacy; meanwhile, the efficacy of efficacy in combination with metformin (rapid release) has been demonstrated in the development of saxagliptin alone; therefore, the combination of relevant clinical applications and data proved that metformin can be better than that of saxagliptin tablets. Its key clinical trials include: BE study through Kombiglyze XR (compound saragliptin metformin sustained-release tablets) and saragliptin tablets and metformin sustained-release tablets, the results showed that the compound preparation and single drug combination when biological equivalent, finally bridging the safety / effectiveness of single drug results, combined better effect, exempted the corresponding confirmatory clinical studies.
However, it should be noted that the domestic project and research results of 2.3 compound preparation, emphasize the product should have clinical advantages, through BA / BE exemption confirmed clinical usually occurs in the development of alternative therapy, generally to improve compliance as the development goal, but compound preparation also has other disadvantages such as dose adjustment, dose dumping risk, when cannot demonstrate the necessity of improve compliance, is not considered to have a clinical advantage.
2、 Loading therapy or the initial treatment
Due to the additive, synergistic and offset effects of adverse effects, the clinical advantage of higher effectiveness and / or safety can be obtained through the development of a new compound of 2.3. Loading therapy and initial therapy are typically developed aiming to improve safety and / or efficacy. Its clinical studies mainly include: sufficient PK study, DDI study, exploratory study, and select the optimal prescription and dose to complete the confirmatory clinical trial.
FDA, the approved AMTURNIDE is a tripartite combination of aligilen, amlodipine, and hydrochlorothiazide hydrochloride. The above three drugs have been marketed as single drugs. This product is a new compound modified preparation, and its clinical research content is shown in Figure 5 [7].
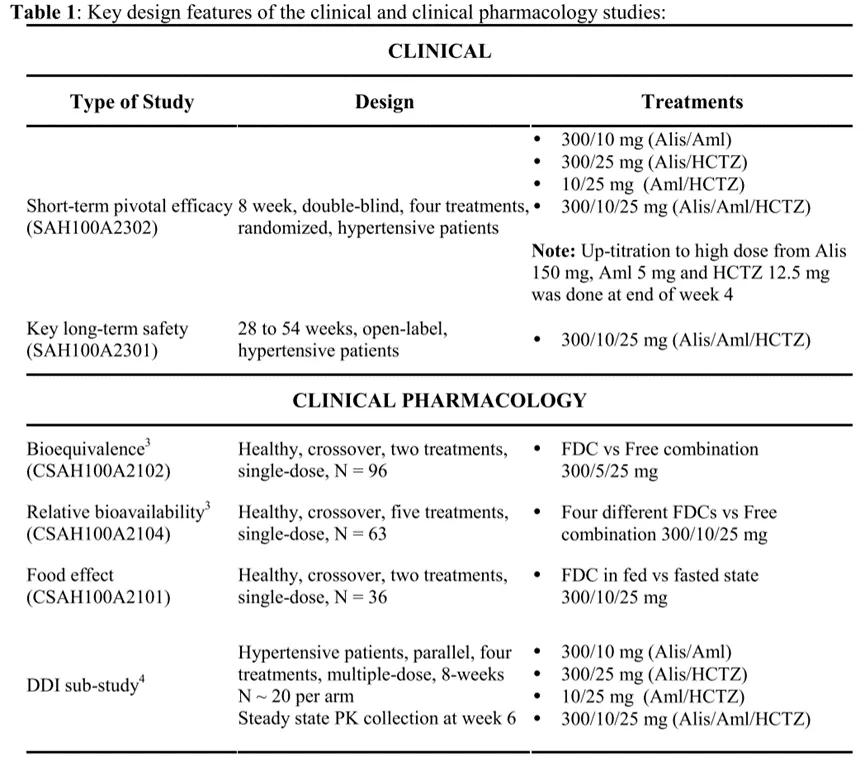
Figure 5 AMTURNIDE
As shown in the figure above, The BE comparison (CSAH100A2102) results show that, Compared with the tripartite combination of this compound preparation, Achlordipine, hydrochlorothiazide hydrochloride, The exposure to Alligene was somewhat reduced, However, according to the volume-effect relationship analysis, It will not affect the efficacy; Food influence (CSAH100A2101) results show that compound amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide hydrochloride are not affected by food, The exposure of aligilen during the postprandial decline, However, according to the volume-efficiency relationship assessment, It will not affect the efficacy; The BA study (CSAH100A2104) compared four different combinations, The optimal party setting and dose were preferred. The drug-drug interaction study (DDI study) and the confirmatory clinical study (SAH100A2302 and SAH100A2301) were further completed with the explored optimal prescriptions and dosages, and the results showed no significant interaction between the three drugs, and the potency study and long-term safety study met expectations and had clinical advantages.
CDE, the approved clinical study strategy and content of cefotaxotam sodium for injection and tazobactam sodium is similar to the above cases, As shown in the review report, The clinical experience: 1) PK study: investigated the PK characteristics of different doses of the product, The AUC and Cmax have a linear pharmacokinetic profile; Distribution volume, half-life and other characteristics are not changed; Compared with the single-agent drugs, There was no change in the body exposure to compound mesefotaxime and tazobactam; 2) The results of the drug interaction study showed that there was no significant interaction between the two drugs; 3) The efficacy and safety study results showed that the efficacy was non-inferior to the pre-modified drugs, Low and lower incidence of adverse reactions, Based on the above findings, Additional safety / efficacy data for single otherapy were approved.
3. 2.3 Other considerations for the development of the new compounds
2.3 The clinical advantages of new compound drugs generally mean that they can improve the efficacy, reduce the adverse reactions, or improve the compliance compared with unilateral drugs.among, Class 2.3 improvements with the goal of improving compliance may be exempt from confirmatory clinical studies through BA / BE testing with combination and preimprovement, However, such improvement needs to demonstrate the necessity of compliance improvement, Such as drugs against HIV, When compliance reached 90%, The viral load can be more than 80% efficient, One or a few omissions of service may lead to a large decrease in response efficiency [4], At this time, the development of compound preparations aiming at improving compliance is considered to have clinical advantages; When the necessity for improving compliance cannot be demonstrated, For example, with the goal of reducing the number of tablets, It is considered a [2] without clinical advantage.
To improve the curative effect or reduce the adverse reaction as the goal of 2.3 improvement, usually based on disease pathogenic factors and pathogenesis, the mechanism of action of each single agent, and the universality of the project [2], compared with known compound molecules development for corresponding isoers, salt, new prescription and other modified way, it is easier to improve in clinical trials. According to the current regulations, guidelines and case analysis, it is known that the improvement of class 2.3 new compound requires rationality demonstration, sufficient PK study, drug interaction study, dose-exposure-effect analysis, and further safety and effectiveness study on the preferred formula and dose. In addition, the exemption or addition of relevant research content should be considered according to the actual situation of drug and disease characteristics, treatment window, patient characteristics, preliminary PK study results, and the opinions of the review institution.
reference documentation:
1. Freije I, Lamouche S, Tanguay M.Review of drugs approved via the 505(b)(2) pathway: Uncovering drug development trends and regulatory requirements.Therapeutic Innovation & Regulatory Science.2020;54(1): 128-138.
2.CDE. Technical guidelines for compound drug clinical trials of chemical drugs.https://www.cde.org.cn/main/news/viewInfoCommon/5c6a7a70f5c5b32319ee4143ce61211
3. CDE. Technical Guidelines for clinical Pharmacology Research of improved chemical drugs (Trial).https://www.cde.org.cn/main/news/viewInfoCommon/25f498093f32286f0f31dbc4d1c8bb43
4. Qian Siyuan, Kang CAI Lian. Clinical considerations regarding compound drug development [J]. Drug administration and Evaluation, 2015,13, (31): 1335-1337.
5. Han Hongcan, Liu Dong, et al. General considerations for clinical pharmacology studies in compound drug development [J]. Drug Administration and Evaluation, 2017,24 (37): 3389-3391.
6. FDA.Kombiglyze XR.CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY AND BIOPHARMACEUTICS REVIEW(S)https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2010/200678Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf.
7. FDA.AMTURNIDE.CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY AND BIOPHARMACEUTICS REVIEW(S).https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2010/200045Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf.




