Disease introduction
As the aging of society accelerates, the number of pain patients is growing globally, and the demand for pain treatment is also increasing. According to a 2018 modification of the definition of "Pain" (Pain) by the International Association for the Study of Pain, pain is now defined as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated or similarly related to tissue damage or underlying tissue damage".
According to physiological basis, pain can be divided into nociceptive pain, neuropathic pain and plastic pain, acute pain and chronic pain. When the pain lasts for 3 to 6 months or more, the acute pain will change to chronic pain, and the risk of mental diseases such as anxiety, depression and sleep disorders will increase, which will seriously affect the quality of life of patients.

According to statistics, the global incidence of pain has reached 35%~45%, its etiology is complex, the mechanism is not clear, not only seriously affects the patients' physical function and quality of life, but also brings great burden to the family and society.
Treatment status
Acute pain is often treated with short-range medications, while chronic pain may require long-acting drugs or other interventions. For mild to moderate pain, choose non-narcotic analgesics; mild to severe pain, usually narcotic analgesics; and a combination of opioid and non-narcotic analgesics may provide additional effects on pain control. Auxiliary analgesic drugs include tricyclic antidepressants, antihistamines and anticholinergic drugs. In addition, there are physical therapy, psychotherapy, patient-controlled analgesia, etc.
Nearly five to ten years of new drugs with CGRP inhibitors, including small molecules and mAb, in 2020 the us listed MOR (opioid receptor μ agonist) class of new drug, in 2019 the American serotonin 1F receptor agonist lacdemitan succinate, in 2019 Japan listed new drug voltage-gated calcium ion channel α 2 δ 1 subunit agonist mililobulalin.
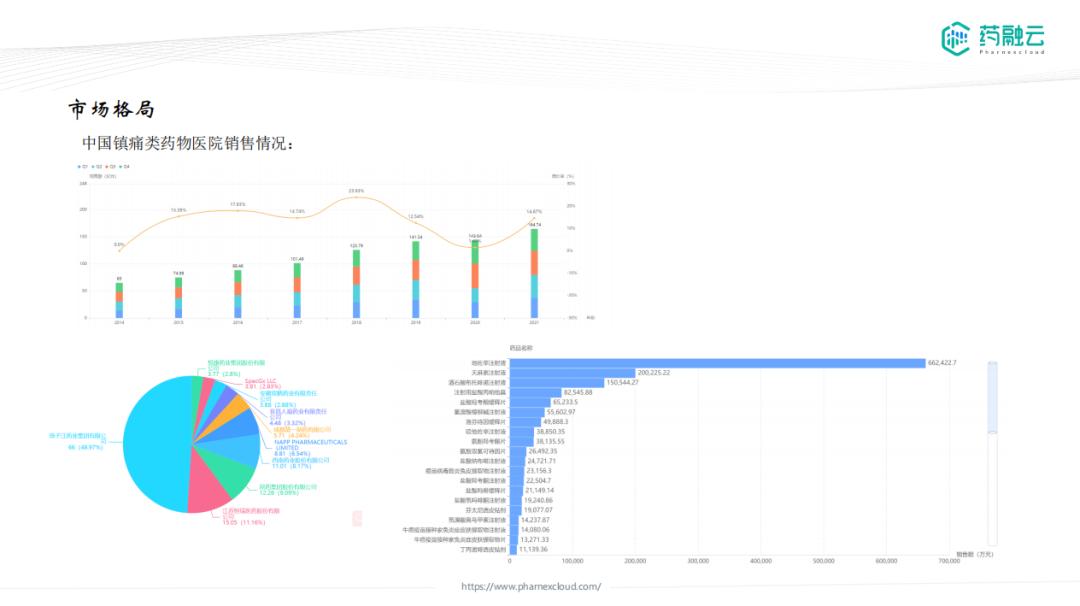
At present, China is the main analgesic drug use country in the world, and the domestic analgesic drugs are mainly opioids, followed by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The domestic analgesic market has great room for growth, lack of varieties and subsequent market sales pattern; the largest analgesic drugs in the American market are several mAbs and small molecules for migraine.
Drugs and potential targets in development
At present, there are more than 400 new drugs in the clinical stage of pain treatment in the world, and there are many varieties in the clinical phase 2 and 3, mainly small molecule drugs. However, there are very few Chinese enterprises, which is not consistent with the huge treatment market in China; it is concluded that the subsequent period of new pain drugs in China is mainly to cause and cooperate in the development of foreign varieties.
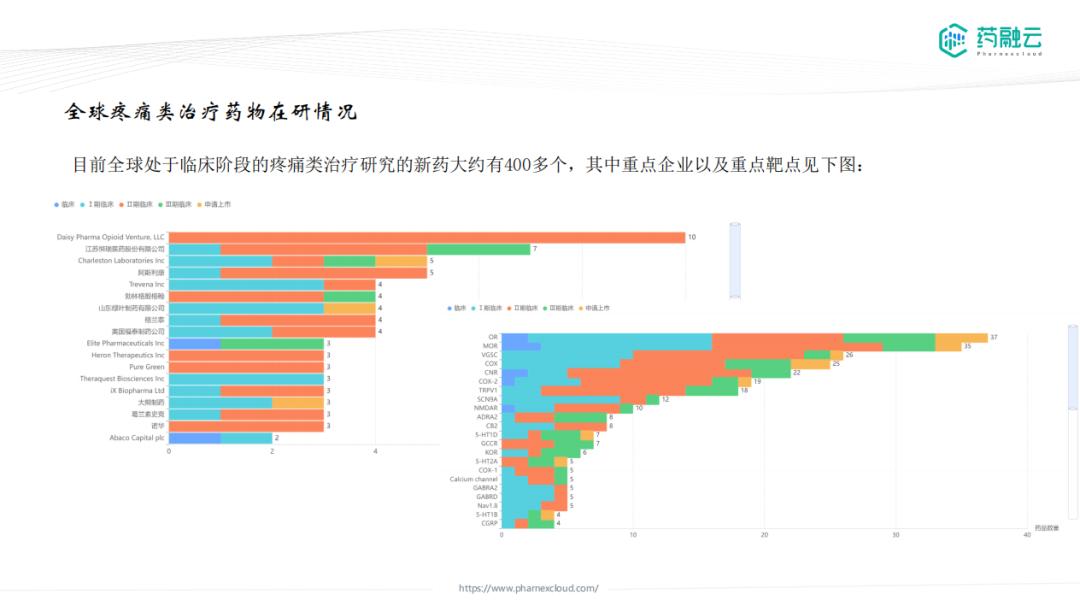
Partial potential targets for pain therapy:
NGF is a neurotrophic factor (neuropeptide), a mediator that causes lasting pain and is released by fibroblasts at the site of injury. After the formation of inflammatory lesions, NGF is rapidly expressed, which can rapidly induce the onset of mechanical and heat-induced nociception. The mechanism of action of this target is clear, and the clinical study data are many, but it has the side effects of antagonists.
TRPV 1 (capsaicin receptor) belongs to the family of transient receptor potential channels, highly expressed on primary sensory neurons and acting as the main integrator of pain stimulation (afferent function) and a key initiator of neurogenic inflammation.
sum up
China is the largest market in the world for pain drugs. However, at present, the treatment of pain drugs has a single mechanism of action, the development of pain drugs lags behind, and the urgent need of new mechanism of action. With more pain treatment drugs on the market worldwide, the direction of pain treatment will be precise treatment based on the types and mechanisms of pain.




